Our Products & Services
Getting Started
First Time Setup
Getting Started With Jobs
Getting Started with Accounts
Getting Started with Inventory
Getting Started with Ticketing
Setting Sonar up for Billing
Baseline Configuration
How To: Using Sonar's Customer Portal
User Specific Resources
Accounts
Account Groups: Overview & Example Use Cases
Account List View: Overview
Account Management View: Overview
Account Overview Customization
Account Statuses: Overview & Example Use Cases
Account Types: Overview & Example Use Cases
Anchor & Linked Serviceable Addresses: Overview and Best Practices
Archiving an Account: Overview
CPUC Fixed Broadband Deployment by Address
Child Accounts: Best Practices & How Tos
Creating a New Account
Direct Messages: Overview
Disconnecting an Account
Disconnection Reason Management: Overview
Exploring Task Groups
FCC Broadband Data Collection (BDC) Filings: How Sonar Can Help
FCC Data Exports: General Overview and Usage
Future Serviceable Addresses: Overview
Lead Intake Form Processing
Notes: Best Practices & Use Cases
Scheduled Events: Overview & Use Cases
Serviceable Addresses: Overview and Usage
Specify Account ID upon Creation
Tasks & Task Templates: Overview
Using Sonar's FCC Broadband Label Generation Tool
Billing
ACH Batching: Overview
Accounts in Vacation Mode
Avalara: Overview & Setup
Batch Payments & Deposit Slips: Overview
Billing Calculator
Billing Defaults
Billing Settings
Building Packages
Building a Data Service
Canadian ACH tool
Changing Service Pricing in Sonar: Best Practices
Considerations When Using Avalara with Voice Services
Creating Discounts for Services and Packages
Delinquency Billing Best Practices
Delinquency Exclusions: Overview and Use Cases
Dual Data Services: Overview
Email Invoice Batch: Overview
General Ledger Codes: Overview
General Transactions: Best Practices
How Sonar Prorates Billing
How to Take Bank Account Payments
How to: Adding a Service to an Account
Invoice Templates: Overview
Leveraging PayPal as a Payment Method in Sonar
Manual Transactions
Multi-Month Billing & Multi-Month Services
Print to Mail
Printed Invoice Batches: Overview
Services: Overview
Setting Up Payment Methods and Taking Payments
Setting up Bank Account & Credit Card Processors
Taxes Setup
Usage Based Billing Policies: Overview and Usage
Usage Based Billing Policy Free Periods: Overview and Usage
Using Tax Exemptions - How To
Communication
Communications: Call Logs Overview & Best Practices
Communications: Messages Overview
Email Variables & Conditions
Message Categories: Overview & Use Cases
Phone Number Types: Overview and Use Cases
Saved Messages: Overview
Setting up an Outbound Email Domain
Trigger Explanations
Triggered Messages: Setup
Using Outbound SMS
Using the Mass Message Tool
Companies
How to: Setting Up a Company in Sonar
Managing Multiple Companies in Sonar: Best Practices
Rebranding your Sonar Instance
Field Tech App
Financial
Contract Templates
Invoice Attachment Use Cases & PDF Examples
Invoice Messages: Overview & Use Cases
Invoices in Sonar: Examples, Creation & Contents
Integrations
Atlas Digital CORE Integration
Calix Cloud Data Field Mappings
Calix SMx Integration: Overview
CrowdFiber Integration
External Marketing Providers
GPS Tracking Providers: Overview
GoCardless Integration: Overview & Setup
How to Connect Cambium to your Sonar Instance
How to Connect Preseem to your Sonar System
How to: Using Webhooks in Sonar
Integrating with Calix Cloud
RemoteWinBox - Integration with Sonar
Sonar Retain: AI-Powered Customer Retention & Quality Intelligence
Tower Coverage Integration: Overview
VETRO FiberMap V2 Integration: Overview
VETRO FiberMap V3 Integration: Overview
Webhooks in Sonar: Basic PHP Example
iCalendar Integration
Inventory
Inventory List View: Overview
Inventory Model Management: General Overview
Network Inventory: How-to & Usage Guide
Segmentable Inventory: How-to & Usage Guide
Setup of Inventory: Manufacturers, Categories, and Assignees
Tracking and Using Consumable Inventory
Jobs
Applying Task Templates to Jobs
Edit Job Options
Example Jobs & Templates
Geofences: Overview
Job Types: Best Practices
Jobs and Scheduling: Overview
Scheduling Dispatcher View: Overview
Scheduling How-to: Creating and Booking a Job
Scheduling Table View: Overview
Scheduling Week View: Overview
Setting Up Schedules General Overview
Mapping
Misc.
Combining Custom Fields & Task Templates for Information Storage
Custom Fields Overview & Use Cases
Custom Links: Overview
Task Templates Overview & Use Cases
Monitoring
Building Alerting Rotations
Building a Monitoring Template
Poller Troubleshooting
Pollers: General Overview, Deployment Strategy, Build Out & Setup
Networking
Adtran Mosaic Cloud Platform Integration: Overview
Assigning RADIUS Addresses
Assigning an IP Address Using Sonar's IPAM: How to
Automating IP Assignments, Data Rates, and Network Access in Sonar
Building Address Lists
Building RADIUS Groups
Building a Device Mapper
Cable Modem Provisioning
Controlling Customer Speeds with Sonar: General Overview
DHCP Delivery
Data Usage Available Methods
Finding your OIDs
FreeRADIUS 3: Build-Out & Integration
How Sonar Communicates - Egress IPs Explained
IP Assignments & Sonar
IPAM: Basic Setup
IPAM: Overview
LTE Integration
MikroTik as an Inline Device: Integration With Sonar
MikroTik: Controlling Access
MikroTik: Controlling Speeds
MikroTik: Setting Up a Sonar Controlled DHCP Server
Netflow On-Premise Integration: Setup and Overview
Network Dashboard: Overview
Network Sites: Management View Overview
PacketLogic: Integration With Sonar
Pulse, Polling, and PHP
RADIUS: Build-Out & Integration with Sonar
RADIUS: Building Reply Attributes
Setting Up CoA Proxy
Sonar Flow
Sonar IP Addressing
Using Multiple Network Devices in Sonar
Purchase Orders
Release Notes
Reporting
Enhanced Business Intelligence - Tips & Tricks for Advanced Users
How To Enhance Your Reporting With Custom Field Data
Report Licenses
Sonar's Business Intelligence: Overview
Understanding Sonar Reports
Using Sonar DataConnect to Connect BI Applications with Your Sonar Instance
Security
Application Firewall: General Overview and Best Practices
Auth0: Overview
Multi-Factor Authentication: Overview
Password Policy In Depth
Removing a Terminated Employee In Sonar
Role Creation using GraphiQL
User Role Creation & Best Practices
Users: Overview
Sonar Billing
sonarPay
sonarPay Canada Disbursements: Overview
sonarPay Chargebacks & Disputes: Overview
sonarPay Disbursements: Overview
sonarPay Monthly Statement: Overview
sonarPay Overview
sonarPay Reversals, Voids, & Refunds: Overview
sonarPay: Token Migration Process
System
A Deeper Dive into the New Sonar API
API Calls Using Third Party Applications: Personal Access Tokens
Browser Compatibility and Minimum Hardware Requirements for Sonar
Consuming the Sonar API
Controlling Your Landing Page: Personal Preferences
Customizing Your Customer Portal
Date/Time Picker: Overview
Dynamic Time Zones in Sonar
Filtering: Overview
Frequently Used Terms
Getting Your Data into Sonar
GraphQL Rate Limiting Overview
How To Use GraphiQL to Understand the Sonar API
How Your Data is Backed Up
How to Best Use Global Search
Interacting with Files via the API
Introducing the New Sidebar
Main Menu: Overview
Mutations in the Sonar API
Notification Preferences
REST API Wrappers for V1 Compatibility
SMS Notifications
Sonar's Rich Text Editor
System Settings: Overview
The New Sonar API
Troubleshooting the Customer Portal
Upgrading your Ubuntu OS - Customer Portal Upgrades
User Profile: Your Personal User Settings
Ticketing
Advanced Ticketing Features
Canned Replies Examples & Templates
Canned Reply Categories
Exploring Ticket Groups
How Sonar Manages Spam Tickets
How to Integrate Inbound Mailboxes with Slack
Inbound Mailboxes Example Build
Ticket Category Families & Ticket Categories: Overview
Ticket Resolution Reasons: Overview
Ticketing: Overview
Using Parent Tickets
Voice
API Changes for Voice Billing
Best Practices to Remain CPNI Compliant
Billing Voice Services in Sonar
Deploying Voice Services in Sonar
Working With the Sonar Team & Additional Resources
Sonar's Security Practices & Certifications
Sonar and General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
Sonar's Security Strategies
Technical Security Overview
Best Practices for Fast Tracking a Support Request
Feedback Portal / Suggest a Feature
Learning with Sonar: Tools and Resources
New Client Training Overview
Sonar Casts Table of Contents
Submitting Bugs vs. Feature Requests
The Sonar Community Forum
The Sonar Status Page
Third Party Customer Support Referrals
Table of Contents
- All Categories
- Billing
- Changing Service Pricing in Sonar: Best Practices
Changing Service Pricing in Sonar: Best Practices
 Updated
by Mitchell Ivany
Updated
by Mitchell Ivany
Read Time: 3 mins
Raising prices is a normal process. Rising infrastructure costs, equipment costs, and backhaul costs all affect your bottom line. These costs need to be considered when billing your subscribers. As a result, cost reevaluation might require a price increase of some or all subscriber services. Deploying these increases could influence the relationship with your subscribers, so knowing your options and minimizing disruptions is of the utmost importance.
Managing Service Pricing
There are two approaches you can take when increasing the price of services offered in your Sonar instance:
- Increasing the price for new subscribers only
- Increasing prices for all subscribers universally
Generally speaking, limiting price increases to new subscribers is far simpler. Limiting the change in this way minimizes the burden of notification, reduces call volume from current subscribers, and still benefits your bottom line. However, it's still worth noting how you can accomplish either or both of these methods.
Increasing Pricing For New Subscribers
When increasing prices for new subscribers, the easiest approach is by disabling the old service, leaving it active on existing subscribers and converting it into a legacy service, then creating a new service.
- Head to Settings → Billing → Services & Packages and Disable the old service.Disabling the service will prevent staff from assigning it to subscriber accounts in the future by removing it as an available option, while leaving it in place for current subscribers. Renaming the service is also an option, however, this change will show up on subscriber invoices.
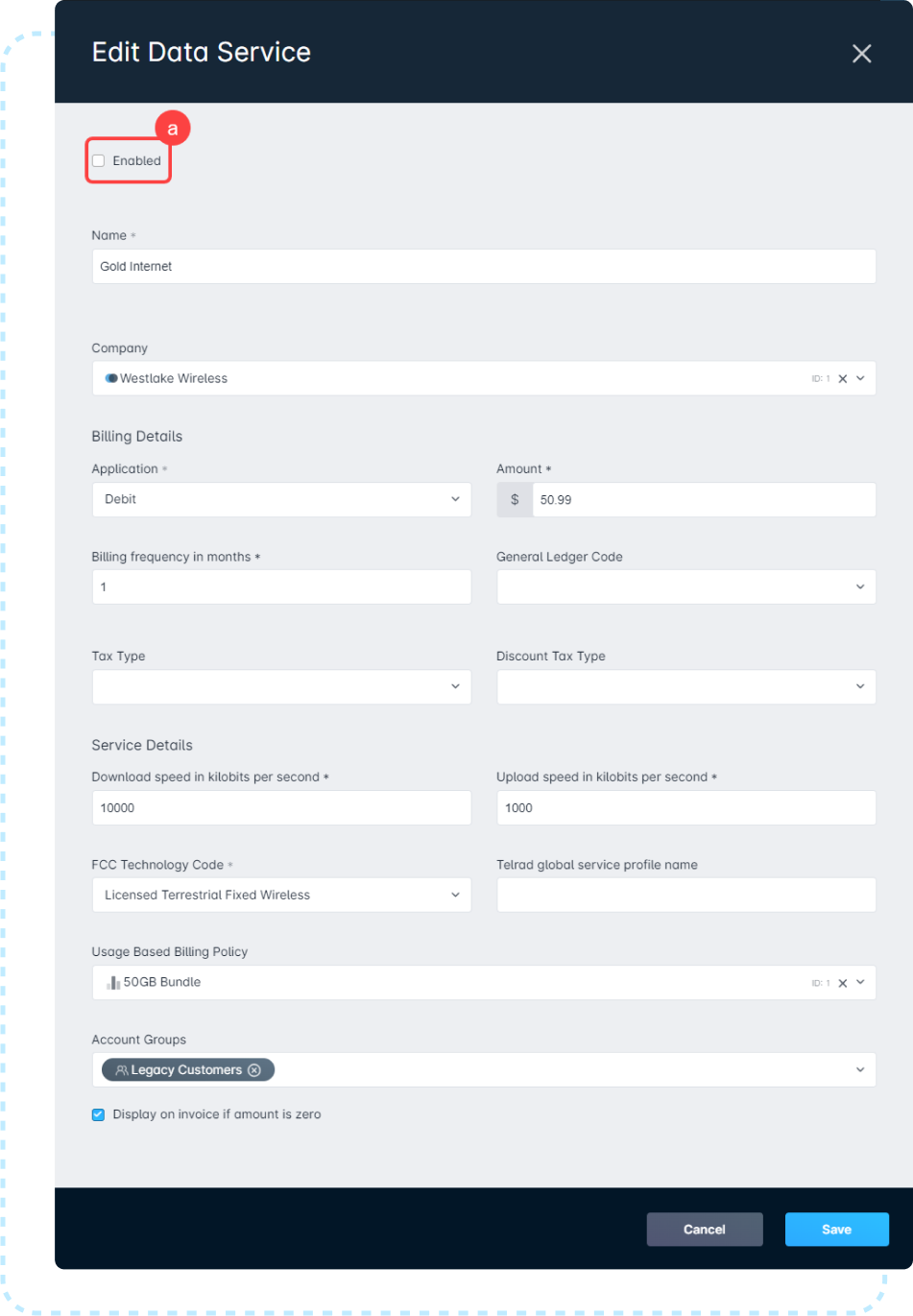
- On the same page, create a new service with the updated pricing. It can reuse the same name as the previous service, as disabling the old service will prevent it from being selected.For instructions on creating a new service, you can check out our Services Overview, Building a Data Service, and Deploying Voice Services in Sonar articles.
Alternative Method For New Subscribers
Rather than deactivating the service, an alternative approach relies on Price Overrides for existing subscribers. This allows you to modify the service directly, without needing to deactivate, rename, and recreate.
- Apply a Price Override to each account that currently subscribes to the service that is being updated.
- This can be done one at a time, or programmatically with the GraphQL API. Depending on the size of your subscriber base, using the API is highly recommended.Doing this operation through GraphQL will only affect one account at a time. If this operation is being performed on a significant number of accounts, consider leveraging automation with Postman or other scripting.
mutation priceOverride($input: UpdateAccountServiceMutationInput) {
updateAccountService(input: $input, id: XXX) {
id
account_id
service_id
quantity
price_override
price_override_reason
name_override
}
}
{
"input": {
"quantity": 1,
"price_override": 9000,
"price_override_reason": "Price Override Reason",
"name_override": "Name Override"
}
}
- This can be done one at a time, or programmatically with the GraphQL API. Depending on the size of your subscriber base, using the API is highly recommended.
- Update the price of the service from Settings → Billing → Services & Packages. The next customer that subscribes to this service will be charged the new price, while legacy subscriptions will maintain the overridden price until they change their service to something else.
Increasing Prices For All Subscribers
Increasing prices for all subscribers is comparatively straightforward, although it should not be done without first notifying your subscribers and your front-line staff of this change.
- Communicate the upcoming price change to your subscribers.
- Depending on the size of your subscriber base, you could notify them on an individual basis. However, it is usually best to leverage a Mass Message, which allows you to email all your subscriber's based on their service.A Mass Message can be used even if you're increasing the price of multiple services. Simply add additional filters to include all services.
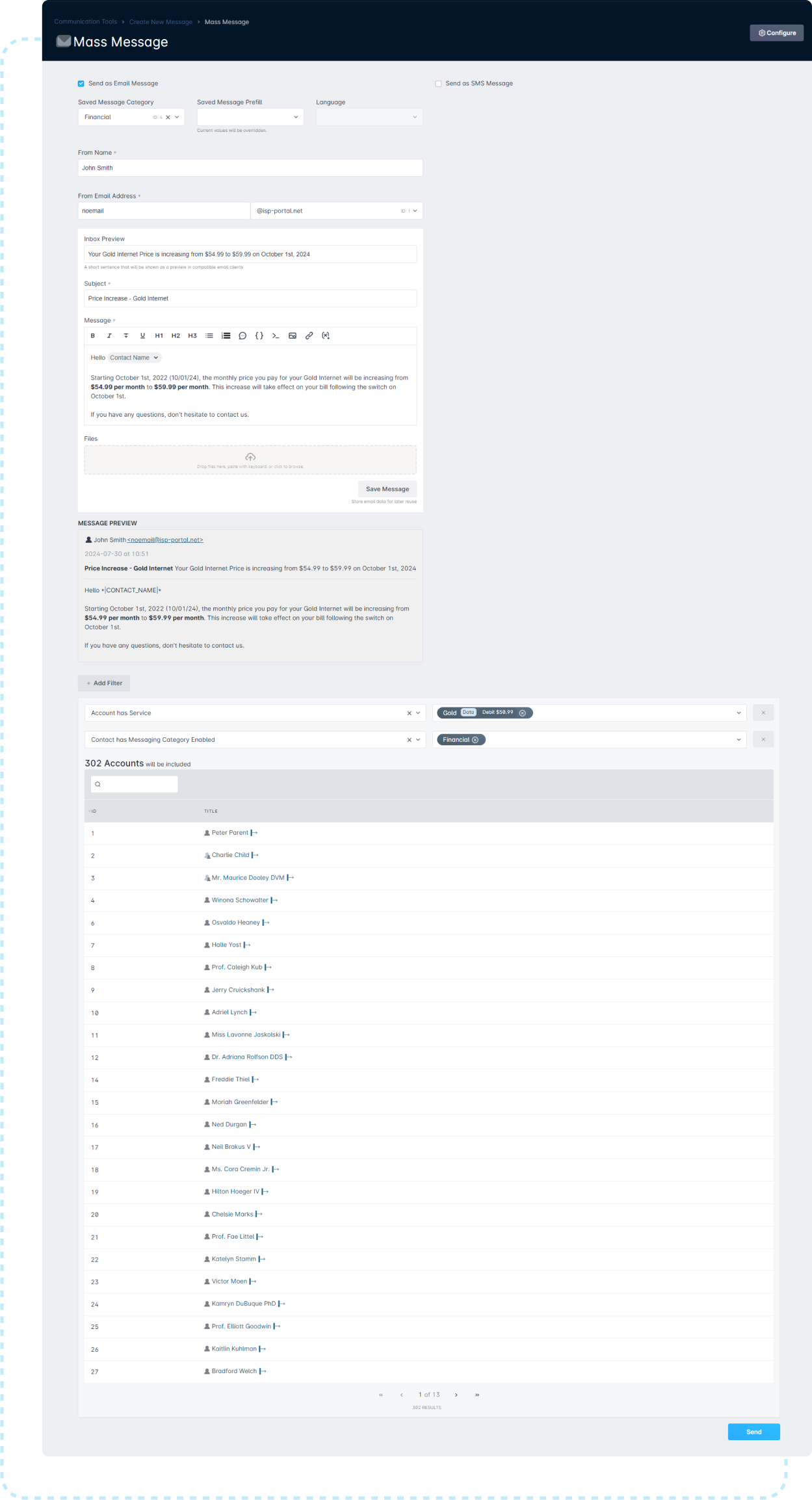
- Depending on the size of your subscriber base, you could notify them on an individual basis. However, it is usually best to leverage a Mass Message, which allows you to email all your subscriber's based on their service.
- Increase the price of the Service in your instance settings. This will charge the increased price to subscribers with this service on any billing runs, starting the next day.When you change the Service Price, you cannot future date the change. Ensure that the price change is only done on the day listed in the notification sent to subscribers.